TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES IN CHILDREN & TEENAGERS-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT. A TWO-YEAR (2009-2011)
Keywords:
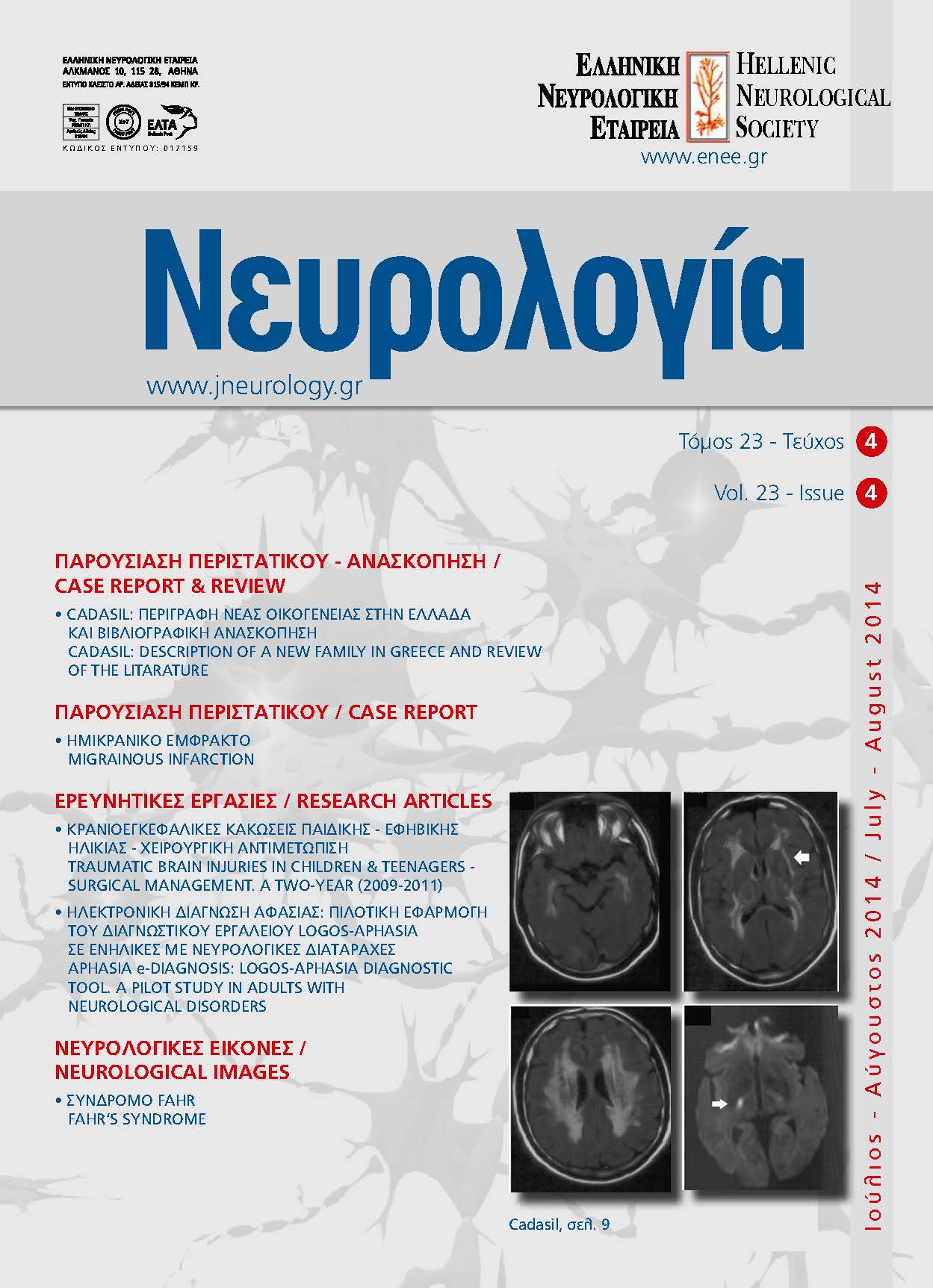
Traumatic brain injuries, surgical management, Thrace, children, teenagersAbstract
Retrospective study of traumatic brain injuries (TBI) affecting children and teenagers in Thrace, Greece. METHOD. During the period 01/01/2009-31/12/2011 82 patients were diagnosed with TBI and treated surgically. Among them, 20 were children and teenagers. Epidemiological data, operative reports and outcome are discussed. RESULTS. Falls, traffic and domestic accidents constituted the major aetiology of TBI. CT images revealed skull fractures, diffuse cerebral oedema, subdural and epidural haematomas. Surgical treatment included craniotomies, craniectomies and intracranial pressure measurements. 2 out of 20 patients (10%) were deceased. CONCLUSIONS. Traffic accidents represented the most common cause of TBI in this age group. Εpidural haematomas were the more frequent lesion. Finally, it is stressed that favourable outcome was strongly associated with prompt surgical intervention.