APHASIA e-DIAGNOSIS: LOGOS-APHASIA DIAGNOSTIC TOOL. A PILOT STUDY IN ADULTS WITH NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
Keywords:
Diagnosis, Aphasia, Neurological Disorders, Diagnostic tools of aphasiaAbstract
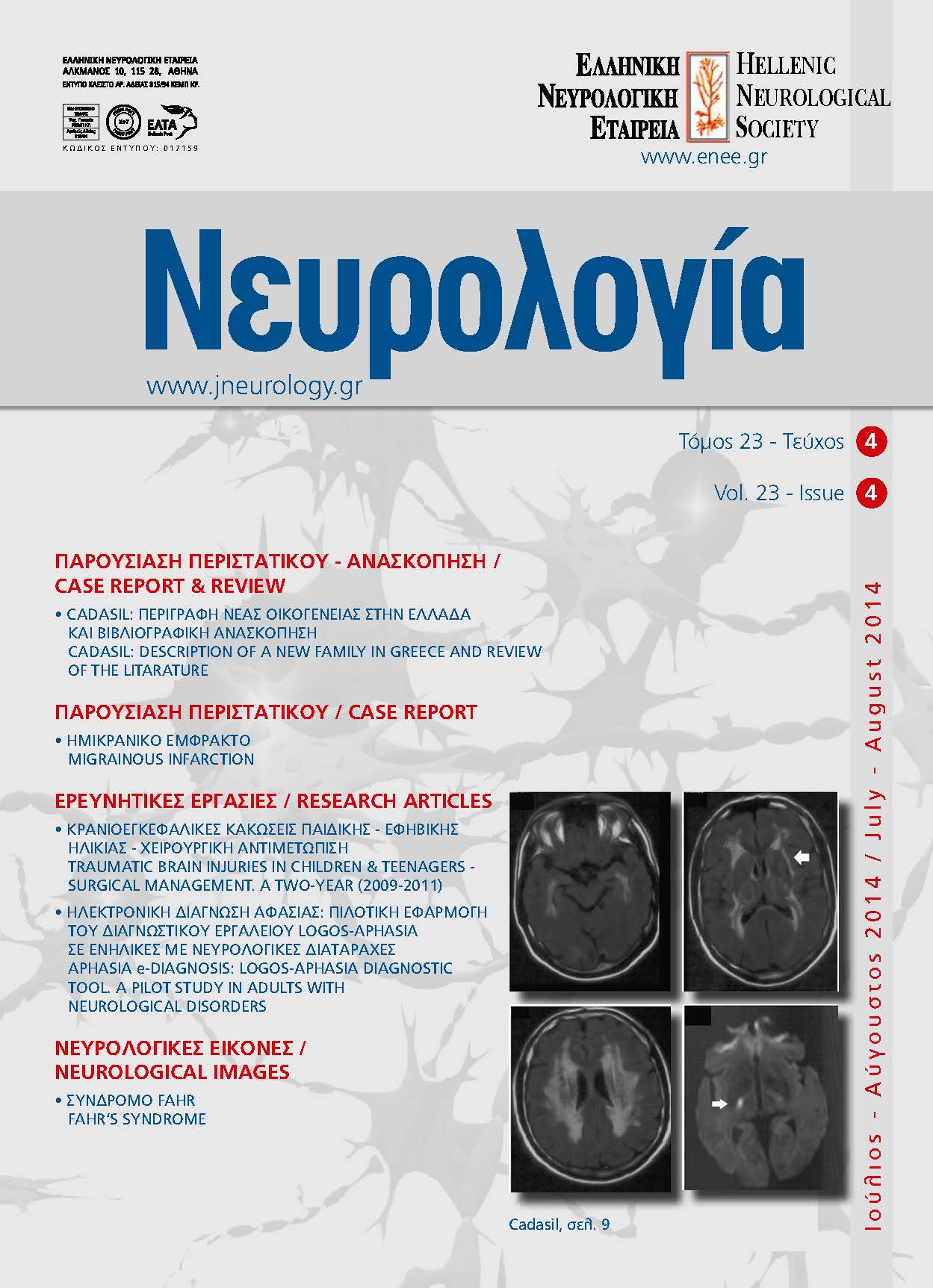
The diagnostic process of aphasia concerns: (i) the diagnosis of presence and type of aphasic syndrome and the identification of damage causing language deficits, (ii) the measurement of performance in language skills and (iii) the profile creation of the patient’s language skills and deficiencies in order to draw a rehabilitation plan. The aim of the research is the study of Aphasia eDiagnosis. In particular, the electronic diagnostic tool LOGOS-APHASIA is the tool to evaluate oral and written language in adults with structural brain lesions. The research sample consists of 23 cases with stroke, brain tumor, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and encephalitis. After collecting medical data (history and images) the diagnostic tool was applied. While strokes constitute the major cause of aphasia (56,5%) in the research sample, aphasia Broca appears to be the most common type of aphasia (30%) and the areas of communication with lower success rates are writing (13%) and cognitive abilities (19%). A detailed report on the results of the study and a discussion on the use of the electronic diagnostic tool follow. Concluding, the aphasia eDiagnosis in conjunction with the clinical practice have the potential to contribute to the diagnostic procedures in aphasia.